Delta Variant Discussion, Vaccine Disinformation, and Misleading Statements from Elected Officials
Threats, Fact Checks, and Reads #7.10.21
Covid
The WHO COVID-19 Dashboard reports 185 million cumulative cases and 4.0 million deaths worldwide as of July 9.
On July 8, the global cumulative mortality surpassed 4 million deaths:
1 death to 1 million- 251 days
1 to 2 million- 114 days
2 to 3 million- 89 days
3 to 4 million- 89 days
Global weekly incidence increased for the second consecutive week, up 3.8% from the previous week. Global weekly mortality, however, continues to decrease down to its lowest point since late October 2020—a decrease of 6.5% compared to the previous week.
Analysis by Reuters indicates that 19 countries* are currently reporting a daily incidence that is 90% or greater of their highest peak.
The US CDC reported 33.6 million cumulative COVID-19 cases and 603,958 deaths.
New daily cases of Covid have increased recently, up from a low of 11,281 new cases per day on June 20 to 14,884 on July 7, a 32% increase—including an increase of 16% over the past week. On July 10, we exceeded 48,000 new cases.
This represents a 430% increase over the low on June 20th of 11,281.
Daily deaths have kept declining although deaths tend to lag behind cases by several weeks, so a rise in cases would not immediately cause an increase in deaths.
The CDC data show that the Delta variant (B.1.617.2) of Covid-19 accounted for 30.4% of new cases for June 6-19.
Delta was number two behind the Alpha variant (B.1.1.7), which accounts for 44.2% of new cases in the same time frame. Delta will likely overtake Alpha because it is rapidly accounting for a larger percentage of new cases.
Delta variant cases have tripled from the two weeks before June 6-19th when it accounted for 10.1% of new cases.
Data in Motion Data Visualization
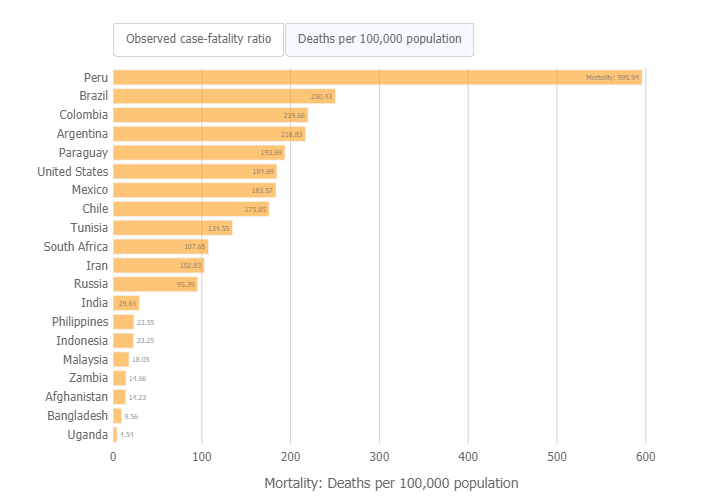
The rate of deaths per 100,000 is worst in Peru by far, but the US maintains its place among countries with far fewer resources and lower average GDP. Brazil, Colombia, and other countries ranking highly in deaths per capita often face obstacles like a lack of sanitation or access to healthcare, something the US was not facing.
Delta COVID variant surges in Asia casts a shadow on Olympics
Scientific uncertainty about Delta and Lambda variants fuels misinformation
The Delta Variant and Vaccines: a mega-thread

Researchers are looking at how well the vaccines protect against the Delta variant, which has caused outbreaks in both vaccinated and unvaccinated communities. It is now the dominant variant in the US.
What We Know for Certain:
Research and real-world data consistently show that unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated people remain at an increased risk of infection and more severe disease.
Everyone who can, should get vaccinated. Every study has underscored the importance of fully vaccinating as many people as possible, especially given emerging variants of interest/concern. More spread = more variants.
Experts are skeptical about the meaning of the data, and real-world data can be challenging to interpret, even for experts. Existing evidence may explain declining protection, but a plausible way of happening is not the same as proof it is happening.
Getting one dose of a 2-step vaccine did not offer strong protection against Delta. The difference between one and two doses was 10% versus 95% protection against the Delta variant. It's that big of a deal.
We want answers now, and some people will exploit this. Scientists who have devoted their lives to this subject want to give answers as soon as they can. They aren't holding back. As soon as they know, they will tell you, but they can't before then.
Association Between Caseload Surge and COVID-19 Survival in 558 U.S. Hospitals, March to August 2020
The surge index was associated with mortality across wards, intensive care unit, and intubated patients. The surge–mortality relationship was stronger in June to August than in March to May (slope difference, 0.10 [CI, 0.033 to 0.16]) despite greater corticosteroid use and more judicious intubation during later and higher-surging months.
Nearly 1 in 4 COVID-19 deaths was potentially attributable to hospitals strained by surging caseload.
Gene Hunters Find Clues That Help Explain Why Covid-19 Hits Some People So Hard
Over the last 15 months, more than 3,300 researchers from 25 countries have poured data from millions of people, including more than 125,000 Covid-19 patients, into the initiative, making it one of the largest gene-hunting missions in history. The international effort has revealed that an individual’s genetic inheritance can indeed influence their risk of infection and the severity of disease.
On Thursday, it was reported in Nature that more than a dozen parts of the human genome were linked with either enhanced susceptibility to infection with SARS-CoV-2 or severe Covid-19. The research won’t change current treatment decisions for patients, but these genetic clues may point to existing drugs that could be repurposed to help the worst-off among them.
WHO's Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline
The WHO has endorsed a duo of rheumatoid arthritis drugs for treating COVID-19 after they showed promising results in reducing the risk of death and the need for mechanical ventilation.
Earlier in the pandemic, researchers suspected that the monoclonal antibodies—tocilizumab and sarilumab—could inhibit deadly immune system overreactions in COVID-19 patients, but individual study results were underwhelming, CIDRAP reports.
However, when combining results from 27 randomized trials covering some 11,000 patients in 28 countries, the drugs revealed their promise.
Compared to corticosteroids steroids alone, hospitalized patients who also received one of the antibodies saw:
A 17% reduction in death
21% reduced risk of mechanical ventilation
Lingering questions: How does this intervention compare to others and what’s the threshold for using it, an accompanying commentary notes.
And, of course, access issues:
“Given the extent of global vaccine inequity, people in the lowest income countries will be the ones most at risk of severe and critical COVID-19. Those are the people these drugs need to reach,” said Janet Diaz of WHO's health emergencies program.
Threats
Elected Officials Rhetoric at Partisan Event Worrisome
The statements made by multiple elected officials raise concerns about the safety of any public health or medical professionals who may try to bring vaccines to low-access areas, particularly any door-to-door efforts. Previously unfounded statements have catalyzed violence in the US.
It’s particularly damaging as the door-to-door offering is one of the best ways to increase vaccine uptake. Anyone may refuse vaccination without giving justification. The aim is to bring vaccines to people who may not have the time or access to it. The strategy is credited with aiding in smallpox eradication.

QAnon Pivots Its Exiled Online Movement to the Real World
The conspiracists might have been de-platformed, but their movement is shifting into local elections and events.
The push for local activity and offline events is a pivotal response to QAnon being deplatformed from the likes of Facebook, Twitter, Reddit, and YouTube. Throughout the weekend, speakers made these removals a key narrative of oppression. Alluding to the deplatforming of QAnon supporters immediately after January 6, one speaker, “Kate Awakening,” called it “the Purge” and said, “it was almost like the scene from Titanic.”
“Us getting together, this was the next inevitable step,” said Brad Getz, a QAnon content creator and another speaker. “They can censor us–you know we’ll just take it on the road then."
Mexico, Brazil, Denmark, Australia, and the US — hard sciences are under attack around the world
Code in huge ransomware attack written to avoid Russian computers
The ransomware also avoids systems that have default languages from what was the USSR region.
Trustwave says the list of countries includes:
Russian (Russia)
Ukrainian (Ukraine)
Belarusian (Belarus)
Tajik (Cyrillic, Tajikistan)
Armenian (Armenia)
Azerbaijani (Latin, Azerbaijan)
Georgian (Georgia)
Kazakh (Kazakhstan)
Kyrgyz (Kyrgyzstan)
Turkmen (Turkmenistan)
Uzbek (Latin, Uzbekistan)
Tatar (Russia)
Romanian (Moldova)
Russian (Moldova)
Azerbaijani (Cyrillic, Azerbaijan)
Uzbek (Cyrillic, Uzbekistan)
Syriac (Syria)
Arabic (Syria)
The Colonial Pipelines attack, carried out by DarkSide, also had a do-not-install list of countries, which was mostly former Soviet satellites and countries with favorable relations with the Kremlin.
Related Read: Biden Weighs a Response to Ransomware Attacks
Trump Sues Facebook, YouTube, And Twitter For Kicking Him Off Their Platforms
China's bid to divide the EU by teaming up with Germany and France
How China Spreads Its Propaganda Version of Life for Uyghurs
A recent investigation by ProPublica revealed a coordinated influence campaign on YouTube designed to counter reports of human rights violations in Xinjiang. The campaign consists of thousands of videos of Uyghurs denying accusations of abuses or forced labor.
The videos contain no logos or signs that they are part of an official campaign, and yet often contain similar key phrases, and were shared on multiple social media channels in a coordinated manner. A similar investigation by USA Today found that a five-part video series spreading disinformation on Xinjiang remained on YouTube for two years before being removed.
#StopAsianHate: Chinese diaspora targeted by CCP disinformation campaign
A report by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute has found that the Chinese state is actively targeting Chinese diaspora communities by co-opting the Stop Asian Hate movement. On multiple social platforms, accounts linked to the Chinese state are repeatedly using the #StopAsianHate hashtag to portray heightened speculation about Covid-19 laboratory-leak theories as part of a broader anti-Asian narrative.
Federal judge largely faults Air Force for 2017 Texas church shooting
A federal judge has ruled that the negligence of the U.S. government and Air Force was mostly responsible for the 2017 mass shooting at a church in Sutherland Springs, Texas, one of the deadliest mass shootings in recent history.
“U.S. District Judge Xavier Rodriguez for the Western District of Texas concluded the Air Force failed to exercise reasonable care when it didn’t submit the shooter’s criminal history to the FBI’s background check system, which increased the risk of physical harm to the general public,” Ashley Killough and Paul LeBlanc report for CNN.
Understanding and Pursuing Information Advantage
Senior leaders across the department have repeatedly expounded on the importance of the information environment for military operations and declared it a priority. Part and parcel of this renaissance surrounding the role of information in military operations are new concepts and terms.
One that is prominent in new foundational documents and frequently appears in stakeholder discussions is information advantage.
This article tries to unpack this concept and explore what it might mean and how it should be thought about by the U.S. Army and the joint force more broadly.
Could Ransomware Become a Geopolitical Weapon? Game Theory Says Yes.
Ransomware is a cheap, easy way to extract concessions from powerful countries—and adversaries are likely to figure that out soon.
Note: The article subtitled that adversaries would figure this out soon, but they already have.
Disinformation
NEWS AND UPDATES
Haitian authorities have said that 26 Columbians took part in Moïse’s assassination.
15 Columbians have been arrested as well as the US-Haitians Solages and Vincent, with all 17 men paraded in front of journalists at a news conference late yesterday. “Foreigners came to our country to kill the president,” Léon Charles said, “there were 26 Colombians, identified by their passports, and two Haitian Americans as well.” Tom Phillips, Peter Beaumont, and Jean-Daniel Delone report for the Guardian.
Related Reads:
Assassination of president plunges Haiti into conspiracy theories, rumor, and fake news
Haiti leader's assassination reawakens Clinton family conspiracy theories
Far-right influencers made thousands of dollars a day on a little-known gaming platform
White supremacist and far-right figures can earn tens of thousands of dollars by streaming their content on the gaming platform DLive.
We knew QAnon is anti-Semitic. Now we know it's racist, too
The vast majority of children who are trafficked originate from the global south. But the images of the children in the QAnon campaigns were almost uniformly white, usually female, and often badly bruised, bound, or bleeding.
Much of QAnon ideology stems from anti-Semitic tropes about elite cabals and blood-drinking pedophiles. It should come as no surprise, then, that QAnon is widely racist, too. But highlighting the extent of that racism may help diminish the spread of QAnon ideology in South America and Africa.
Related Read: Russia Amplifying Critical Race Theory. Iran, China Mum on the Subject.
Note: Discussing the theory at all is the product of media manipulation and further amplifying a manufactured controversy would be unwise. That said, people have heard about this and want to know what it is, so it’s included. It’s a graduate-level academic theory that isn’t and never was going to be in K-12 schools in the US.





Hunting down bots and 'bad guys' on social media
Diogo Pacheco is a bot-hunter. For the uninitiated, bots are the ground troops of social media, autonomous accounts that post, tweet, or retweet. Some bots are harmless: sharing pictures of cats or jokes. Others, however, look like actual users and can engage in political or disinformation campaigns.
With the University of Exeter and the Observatory on Social Media and Center for Complex Networks and Systems Research at Indiana University, Pacheco studies inauthentic activity online and examines how fake conversations and coordinated online networks can change our opinions and the way we think. Bots and fake accounts, which have invaded online conversations on everything from the coronavirus vaccines to the human rights crisis in Xinjiang, have been at the center of the debate about disinformation since President Trump was elected in 2016 and the UK’s Brexit referendum in the same year.
Coda spoke to Pacheco about how he tracks bots and fake social media behavior. This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Climate scientists take swipe at Exxon Mobil, industry in a leaked report
A top lobbyist for the oil major was caught on camera acknowledging working with groups engaging in disinformation campaigns.
Related Read: Big Oil's lies about climate change—a climate scientist's take
We know now that fossil fuel company researchers understood early on, from their own work as well as that of academic and government researchers, that warming due to human emissions of greenhouse gases posed risks at the planetary scale.
If a company were to dump toxic waste in your backyard, making the air you breathe and water you drink hazardous, they’d be liable for the harm they caused you. (Of course, fossil fuel companies have done exactly this also, in many places around the world, and often faced little consequence, particularly when the victims are from poor and marginalized communities.)
Increasing carbon dioxide concentrations globally doesn’t poison us, but it’s still broadly analogous to this backyard example—except on the scale of the entire planet. Instead of giving us cancer or heart disease, the increase in carbon dioxide emissions is making essentially irreversible changes in the environments in which we all live, such that they deviate from those to which our civilization is adapted.
From Novel Science
Vatican launches all-out effort to combat vaccine hesitancy
The Vatican’s bioethics academy and the World Medical Association on Friday called for an all-out effort to combat vaccine hesitancy and correct the “myths and disinformation” that are slowing the fight against the coronavirus.
In a joint statement, the groups said some vaccine reluctance in poorer countries is rooted in historical inequalities and suspicions of Western pharmaceutical companies. But they said “a more pernicious form” of hesitancy is being driven by fake news, myths, and disinformation about vaccine safety, including among religious groups and some in the medical community.
They demanded that “all relevant stakeholders exhaust all efforts to ... confront vaccine hesitancy by sending a clear message about the safety and necessity of vaccines and counteracting vaccine myths and disinformation.”
The statement also repeated calls from the Vatican and the medical establishment for vaccine equity, to make sure the poorest nations have the same access to shots as wealthier ones.
FACT CHECKS
All fact-Checking initiatives in Europe
No evidence of ‘graphene oxide’ that’s ‘toxic’ in Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine
An Instagram post with an incendiary video claims that Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine is dangerously packed with something called graphene oxide. No evidence was provided for the claim.
Pfizer says it does not use graphene oxide and no such ingredient is listed in any of the three COVID-19 vaccines authorized for use in the U.S.
Related Read: COVID-19 Vaccines Do NOT Contain 99% Graphene Oxide To Conduct 'Mass Poisoning'
Texas GOP Rep. Ronny Jackson says the potential for door-to-door vaccination services ‘fits right into the narrative’ of Democrats’ ‘socialist, Marxist, communist way they want to control your lives’ during an appearance on Fox News.
Rep. Jackson provided no evidence to support his claims that door-to-door vaccination services relate to a greater agenda. It’s unclear how a relatively common public health measure, used here and in other areas of the world, ties to socialism or Marxism.
Historically healthcare was provided in homes, with the house call ceasing in favor of hospitals in the past century.

Past door-to-door efforts have dramatically increased vaccination rates and decreased children dying from disease. Neither house calls nor door-to-door vaccinations were associated with a societal drift toward Marxism or socialism. Door-to-door campaigns were associated with declines of infectious disease and eradication as was the case with smallpox.
Either Rep. Jackson is unaware of the definition of the terms he used in which case this would be misinformation, or he knows the terms don’t apply or relate, which would make this disinformation.
Russia's US Embassy Distorts What Happened in Republican Party Cyber-Attack
On July 6, Bloomberg reported that a Russian intelligence-linked hacker group had breached computer systems used by the Republican National Committee. The attack, attributed to Cozy Bear, also known as APT 29, came around the same time as a wider Russia-linked ransomware attack on a U.S. technology firm, Kaseya VSA, that affected hundreds of American and European companies. No link between the two attacks has been reported.
Bloomberg initially reported that an RNC spokesman had denied the breach had taken place. However, after the story was published, RNC chief of staff Richard Walters told the news agency that Symnex Corp., a California-based IT services contractor used by the RNC, had in fact been breached. The RNC did not say whether any data was stolen or otherwise compromised.
Russia’s Foreign Ministry seized on the RNC’s initial denial of an attack, with the Russian Embassy in Washington D.C. denying any involvement in the attack and questioning whether the RNC attack had taken place.
Covid-19 and flu comparisons reappraised
No, they’re not the same. No, the seasonal flu is not less deadly. We’ve been over this before, but here we go again.
Dr. Sherri Tenpenny Interview Is Full Of False, Misleading Claims About COVID-19
The interview, which appeared on the "Stew Peters Show," is full of false and misleading claims. For example, Tenpenny alleges that COVID-19 vaccines are not effective, that they cause harm, and that they make our bodies magnetic. None of those claims are correct, as shown by prior fact checks, and all are missing important context. Tenpenny also alleges that COVID-19 and the vaccines are part of a grand plan to control the world's population. There is zero evidence that conspiracy theory is true.
The Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 has become prevalent in the U.K. since May 2021. At the same time, most of the people who are vaccinated in the U.K. are the elderly, who were among the priority groups in the COVID-19 vaccination campaign, as they are at a higher risk of severe illness. So far, the data shows that most COVID-19 cases caused by the Delta variant in the U.K. occur in people under 50 years old, an age group that is less likely to die from COVID-19 compared to those older than 50.
As most of the risk groups in the U.K. are now protected by vaccination, fewer people are expected to die from a Delta variant infection. Therefore, while the fatality rate of the Delta variant appears lower, this is a result of vaccination and the characteristics of the unvaccinated population, and not necessarily because the Delta variant is less lethal than the wild-type virus.
Covid-19 mutated long before mass vaccine roll-outs
Retracted Study Used to Discredit COVID-19 Vaccines
A now-retracted study published in the scientific journal Vaccines is being hailed as proof that COVID-19 vaccines are dangerous. The study was retracted for misrepresenting data from the Netherlands’ vaccine adverse reaction reporting system, Lareb, to conclude that the COVID-19 vaccines cause two deaths for every three deaths they prevent.
As with the VAERS system in the U.S., anyone can report any adverse reaction following vaccination to Lareb, whether or not it was actually caused by the vaccine. The data collected by these reporting systems are meant to monitor and investigate potential adverse reactions, not to represent verified vaccine side effects.
The Public Health Collaborative recommends ignoring this misinformation but should you encounter false claims, here is a fact check article: Flawed Paper on COVID-19 Vaccines, Deaths Spreads Widely Before Retraction
Research
Tucker Carlson claims the NSA is spying on his show. The NSA says it isn't and Carlson has provided no evidence, excepting his word to bolster the claims.
In the case of the Tucker Carlson-NSA claim key amplifiers of the story were:
US elected officials,3



Intention cannot be assessed with any accuracy at this point, but this particular story could potentially:
increase mistrust about the findings of any investigation into the Jan 6th attack on the US Capitol, which may have involved members of Congress,7
cast doubt on serious allegations of sex trafficking of minors by Rep. Matt Gaetz,8
stoke paranoia and fear, which may leave people less able to critically assess claims about censorship and persecution, and9
promote violence in the future by creating the perception of a serious threat.10
Note that this does not assert or imply this is the intention of those amplifying the claims, but these are possible consequences regardless.
Euro track: majority in EU support new EU Digital COVID Certificate for travel
The new certificate acts as a vaccine passport, and allows travelers to prove that they have met at least one of three criteria:
they have been vaccinated against COVID-19,
they have received a negative test result, or
they have had the virus and recovered.
Anyone legally living in countries that recognize the certificate (all EU members, plus Switzerland, Iceland, Norway, and Liechtenstein), is eligible to use the scheme.
How investigative journalists can generate support for fighting anti-Semitism
High-profile investigative journalists openly challenged their traditional boundaries to allow for more open, activist exposés to confront Holocaust hate speech. Their performances resembled enthusiastic activists by being connected and twittering during the ‘hot moments’ of challenging Holocaust denial. This pursuit was particularly evident during the US presidential campaign in 2016 and its aftermath as investigative journalism became a political act in a struggle over the meaning of neo-Nazis’ roles on social media networks.
Other journalism communities responded to the investigative journalists’ self-reflexivity by reaffirming and magnifying their performances. These communities were involved in an ongoing process of challenging the social media boundaries of their profession. They discarded their support for the boundaries that separated them from trolling to pursue activist-like agendas that focused on exposing neo-Nazism as well as the myths involving Holocaust denial. Through informal networks, their performances showed their continued experimentation to begin turning back the tide of trolling.
Investigative journalists indicated the liberating potential for more direct, open challenges to anti-Semitism and Holocaust denial in the media. Their roles as anti-Nazi activists and troll hunters marked a turning point in the struggle to start overturning the chilling effect of trolling and online hate speech. The innovative exposés generated other journalism community members’ support to engage in a cooperative search for fresh solutions to promote greater social cohesion within the online networks. Their work suggests investigative journalists’ crucial leadership in initiating a collective call to action to enhance the inclusive community ideals of civil society on popular social media networks.
-Coatney, C. (2021). Don’t feed the trolls? Cosmopolitan Civil Societies: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.5130/ccs.v13.i1.7421
YouTube's recommendations still push harmful videos, crowdsourced study finds
A new crowdsourced investigation from the Mozilla Foundation, the nonprofit behind the Firefox web browser, asked more than 37,000 YouTube users to act as watchdogs and report harmful content through a browser extension that was then analyzed by research assistants at the University of Exeter in England. That user-supplied content included Covid-19 misinformation, political conspiracy theories, and both violent and graphic content, including sexual content that appeared to be cartoons for children, the analysis found.
A majority — 71 percent — of all the reports came from videos recommended by YouTube’s algorithm and recommended videos were 40 percent more likely to be reported than intentionally searched-for videos, according to the report. Reported videos also outperformed other videos, acquiring 70 percent more views per day than others watched by volunteers.
UN ‘Pause’ campaign slowed the spread of life-threatening misinformation
A major part of that work is the UN!s Pause campaign, which encourages people to pause to check the validity of any information they share. Now, a new study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) says the Pause campaign can bring about the behavioral change needed to stop the spread of misinformation.
The MIT study, conducted in the UK and the US, found that the simple act of pausing to question the origin, credibility, relevance, and accuracy of any information before sharing it on phones, computers, and social media platforms, significantly reduced people!s propensity to share misinformation. In the study, participants who saw Pause campaign content were notably less likely to share fake headlines.
Also See: UN Pause
European support for Dutch-Flemish project in the fight against disinformation
Covid Origins Mirror SARS’s Genesis in Animals, Study Finds
Early Covid-19 cases traced to markets in Wuhan, China, mirror the initial spread of SARS 17 years earlier, scientists said in a paper that concludes that an animal contagion is the most likely explanation for the pandemic’s genesis.
The epidemiological history of the SARS-CoV-2 virus is comparable to previous animal market-associated outbreaks of coronaviruses and offers a simple route for human exposure, Edward Holmes, Andrew Rambaut, and 19 other researchers said in a review of the scientific evidence pertaining to the pandemic’s origins.
The paper was released Wednesday ahead of peer review, and is being prepared for submission to a journal for publication, one of the authors said. It gives a detailed explanation for SARS-CoV-2’s genetic signatures, early epidemiology, and research undertaken at the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
Violent Extremism in America: Can It Be Stopped?
Co-authors of the RAND report, Violent Extremism in America, discuss the findings from their interviews with former members of radical organizations. They identify pathways to radicalization and propose methods for preventing the radicalization of individuals and for deradicalizing those already in extremist organizations.
Earlier this year RAND took the approach it has used in suicide research and applied it to the study of radicalization. The results provide a window into the experiences of families who have had someone radicalize as well as the people themselves.
Key Findings from the RAND report
Negative life events are part of, but not the sole cause of, radicalization. Abuse or trauma, difficult family situations, bullying, and other negative life events often have psychological and behavioral consequences and are sometimes implicated in radicalization pathways.
Those with mental health challenges often had difficulty accessing care because of cost or inaccess.
This may have left them more vulnerable to recruitment.
The enduring appeal of extremist groups seems to lie in attending to fundamental human needs.
Many were seeking social bonds, love, and acceptance.
Radical ideology and involvement in extremist activities have addictive properties for many. They are drawn to the struggle against a common enemy.
Recruitment to radical groups deliberately leverages psychological vulnerabilities
Radical groups develop ways to bolster ideological commitment
(1) through restriction of access to information or circumstances that challenge the radical ideology--also known as information and thought control in the BITE model of authoritarian control--and
(2) by using evidence-based social and psychological manipulation methods for reinforcing hatred toward the outside the group.
Extremist groups nurture a self-reinforcing social milieu, which includes shared purpose, friendship, shared activities which involve sharing both risk and reward.
Both radicalization and deradicalization are linked to "being in the right place at the right time.”
Heavy-handed attempts by formal institutions to de-radicalize individuals often fail. Measures by intelligence and law enforcement can sometimes worsen the problem and drive people toward even more extreme behaviors.
Stigmatization of groups seems mostly to push at-risk individuals further down the extremist path. Banned speech and punitive measures may increase the drive for radicalization.
Media literacy, access to diverse sources of information, and positive experiences with people from different social and cultural backgrounds appear critical for deradicalization. Outsiders who showed kindness and generosity had positive effects but the behavior of radicalized or radicalizing individuals often repels people and deters others from approaching with compassion.
Related video: Exiting Extremism: What Binds People to Extremist Groups and How Organizations Help Them Leave
Recommended Reads
For ten years, the United States military has defined cyberspace as the fifth domain of war, equating it with the four physical domains of warfare as a core planning assumption.[1] But classifying cyberspace as a domain is fatally flawed both because it obscures the purpose of recognizing the four physical domains, and because it unnecessarily puts cyber into too small a box.[2] The buzzwordification of the term domain has long passed the point of diminishing returns and nowhere is that a greater hazard than with cyber operations.[3] It’s time to re-think cyber to reflect the realities of modern war and with it the broader lexicon of what constitutes domains and layers of warfare.
This article proposes the United States re-focus the definition of domains of warfare on the four physical domains, which require distinct organizations and doctrines to effectively control and exploit while elevating the parallel concept of functional multi-domain operations such as Special Operations and Cyber Operations with fixed representation at the Undersecretary of Defense level. This is necessary not because denying cyberspace or information as a domain would diminish its importance, but because it is a flawed analogy that both undercuts the need for the current service structure and would treat cyber as a separate pillar of defense.[4] It implies cyberspace should have an independent service—which is the wrong solution to the growing all-domain challenges of cyber operations.[5]
The Smoke Comes Every Year. Sugar Companies Say the Air Is Safe.
They also worked closely with six experts in air quality and public health from universities across the country, including three in Florida, as well as with residents, to place outdoor air sensors that measured particulate matter.
The measurements were not intended to assess compliance with the Clean Air Act. Rather, the goal was to see if residents were being exposed to pollutants in ways that current monitoring systems would miss.
They were.
While American sugar executives argue they can’t overhaul their processes, the country is an outlier on the global stage. The U.S. is the fourth-largest sugar producer in the world. China is the only other top-five sugar-producing country that hasn’t moved to end cane burning.
Spy Agencies Turn to Scientists As They Wrestle With Mysteries
The nation’s intelligence agencies are looking for ways to increase their expertise in a range of scientific disciplines as they struggle to answer unexplained questions — about the origins of the coronavirus pandemic, an unidentified phenomenon observed by Navy pilots, and mysterious health ailments affecting spies and diplomats around the world.
Traditional spycraft has failed to make significant progress on those high-profile inquiries, and many officials have grown convinced that they require a better marriage of intelligence gathering and scientific examination.
Events
Submit events for consideration by emailing editor @ Novel - Science.com with full details.
14 July
Online Seminar: Safeguarding the Wellbeing of Your Workforce - A Briefing on Hate Crime
18 July
Virtual Discussion - A Forum on Antisemitism and other Hate Crimes in Orange County
19 July
Virtual Discussion - National Forum Supporting Legislation to Combat Online Hate
23-25 July
8th International Conference on Research in Behavioral and Social Sciences
4-6 November
Information about Gonzaga University’s Sixth International Conference on Hate Studies: “Justice and Equity: Challenging Hate and Inspiring Hope” 4-6 November 2021, Spokane, USA available here.
Registration is open for the upcoming “5th International Conference on Social Science, Humanities and Education”. The conference is taking place in London, UK on 27-29 August 2021. Find more information and book your place by 20 August 2021 here.